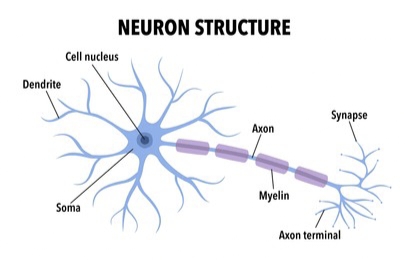
Neuron: A specialized cell that transmits and processes information through electrical and chemical signals, forming the basic unit of the nervous system.
Principle of a Neuron
Neurons operate on the principle of electrochemical transmission.
They carry messages by converting stimuli into electrical impulses.
Communication happens within neurons (electrical) and between neurons (chemical).
Parts of a Neuron
Cell Body (Soma): Contains the nucleus; maintains cell function.
Dendrites: Receive incoming signals from other neurons.
Axon: Transmits impulses away from the cell body.
Myelin Sheath: Fatty covering that speeds up signal transmission.
Axon Terminals: Ends of the axon that pass signals to other neurons or cells.
Synapse: Small gap where neurotransmitters carry signals between neurons.
Functions of Neurons
Sensory Function: Detects stimuli (e.g., light, sound, touch) and sends information to the brain.
Integrative Function: Processes and interprets sensory input in the brain and spinal cord.
Motor Function: Sends instructions from the brain to muscles and glands.
Location in the Human Body
Brain: Billions of neurons form complex networks responsible for thought, memory, emotion, and coordination.
Spinal Cord: Neurons relay messages between the brain and body.
Peripheral Nerves: Neurons extend throughout the body to sense the environment and control muscles.
Key
Neurons are vital for every movement, thought, and feeling. Understanding their structure and function helps us grasp how the brain and nervous system work together to control the human body.