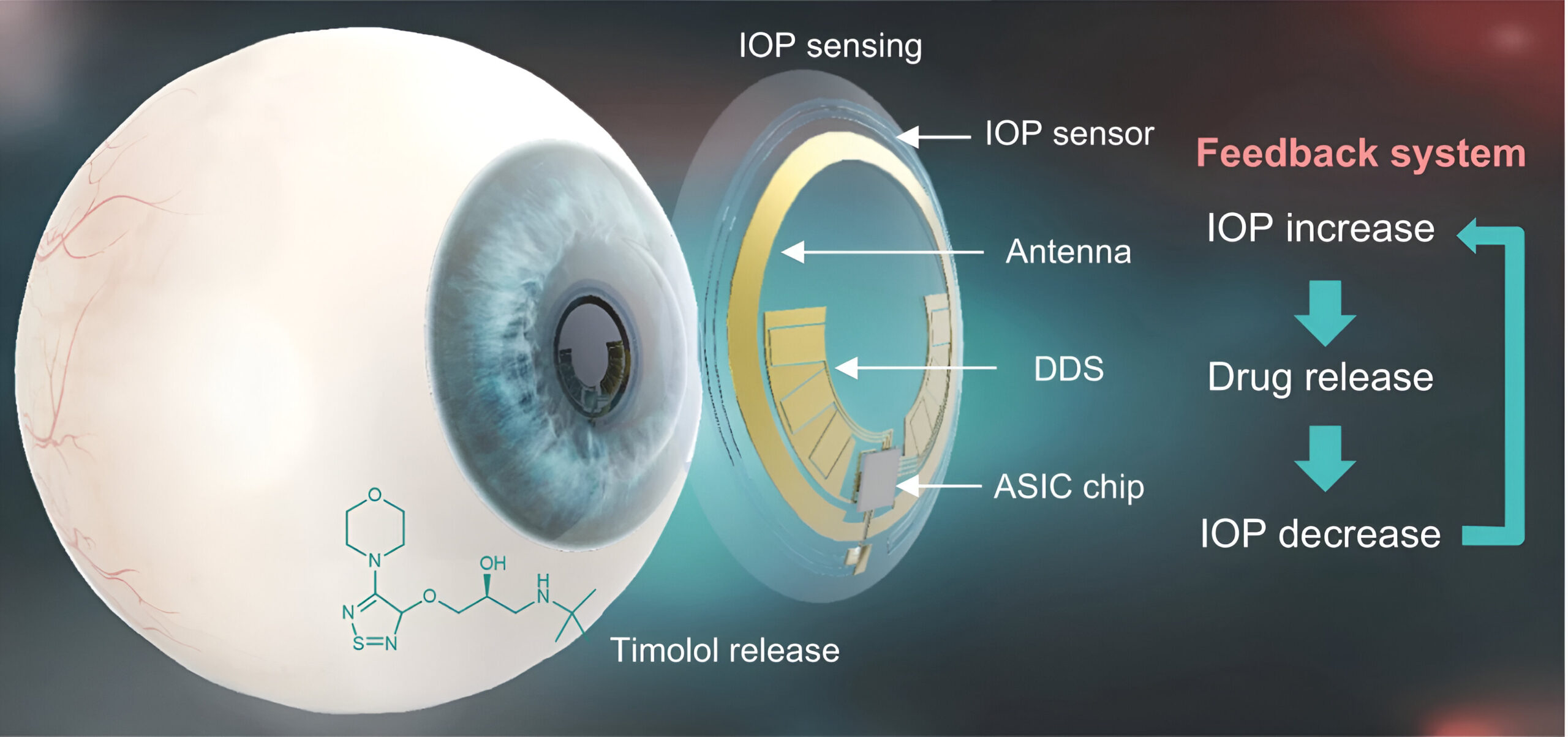
What if your contact lenses could not only correct your vision but also monitor your health, project digital information, or even treat diseases? This is no longer science fiction—smart contact lenses are emerging as one of the most exciting frontiers in both optometry and wearable technology.
Let’s take a closer look at how smart contact lenses work, the cutting-edge technology behind them, and the incredible possibilities they hold for the future.
What Are Smart Contact Lenses?
Smart contact lenses are next-generation wearable devices that integrate microelectronics, sensors, and wireless communication systems into a soft, biocompatible lens. These lenses can do much more than just correct refractive errors—they have the potential to:
-
Monitor health conditions in real-time
-
Deliver medications directly to the eye
-
Display augmented reality (AR) data
-
Track intraocular pressure (IOP) for glaucoma
-
Control myopia progression
The Science Behind It
Smart lenses combine several advanced technologies:
-
Miniature sensors (for glucose, IOP, temperature)
-
Micro-LED displays (to project images onto the retina)
-
Wireless chips (for data transmission)
-
Energy harvesting systems (such as solar or radio frequency)
-
Drug delivery reservoirs (to treat eye diseases like dry eye or infections)
These elements are embedded in ultra-thin, flexible substrates to ensure comfort and safety.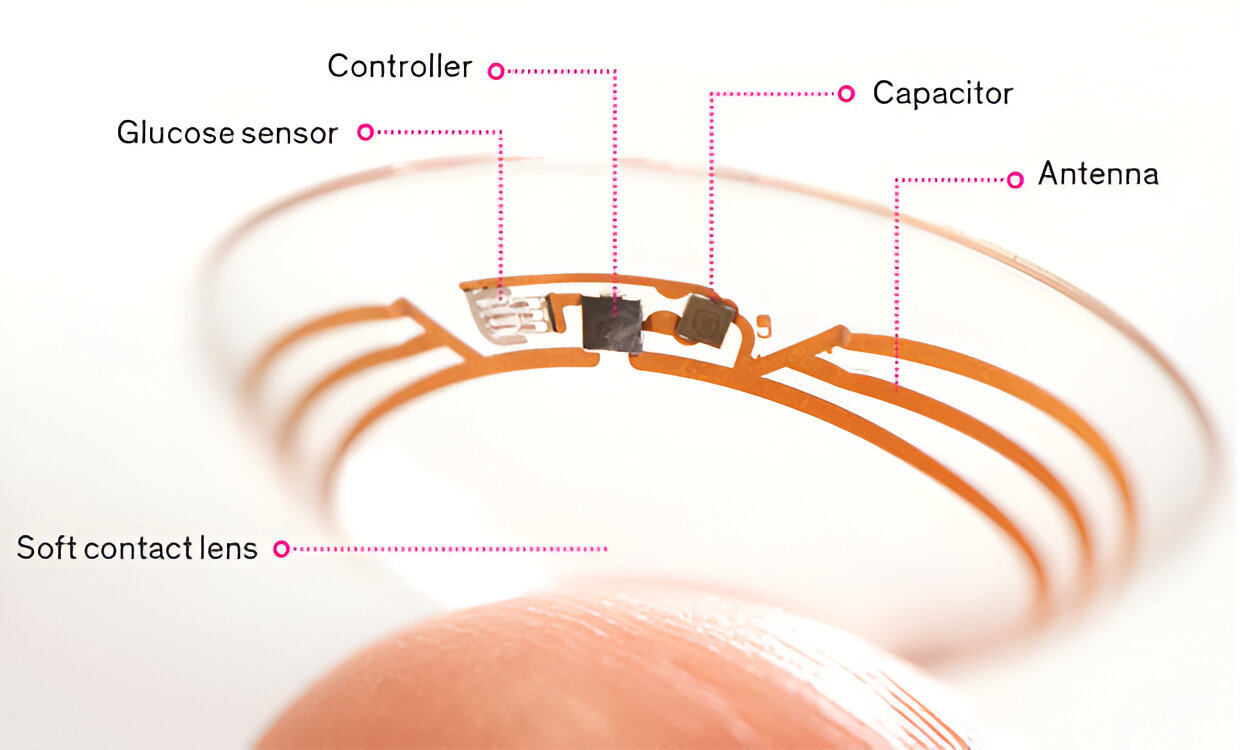
Current Developments and Prototypes
Several tech giants and research institutions are racing to bring smart lenses to life:
1. Mojo Vision
-
Developed the Mojo Lens, a contact lens with a built-in microdisplay that can show information like navigation, notifications, and fitness data—all while remaining invisible to others.
2. Google/Verily’s Smart Lens Project
-
Initially focused on glucose monitoring in tears for diabetic patients.
-
Although shelved due to technical challenges, it spurred global interest and research in tear-based diagnostics.
3. Samsung and Sony
-
Working on lenses with embedded cameras and AR capability, possibly integrating with smartphones or smart glasses.
4. University & Industry Collaborations
-
Institutions like EPFL (Switzerland) and Stanford University are creating lenses to monitor IOP, drug delivery, and eye biometrics.
Medical Applications
The most promising aspect of smart lenses lies in healthcare, especially in optometry and ophthalmology:
Glaucoma Monitoring
-
Lenses with pressure sensors can continuously monitor IOP, helping patients and doctors manage glaucoma more effectively than occasional office measurements.
Diabetes Management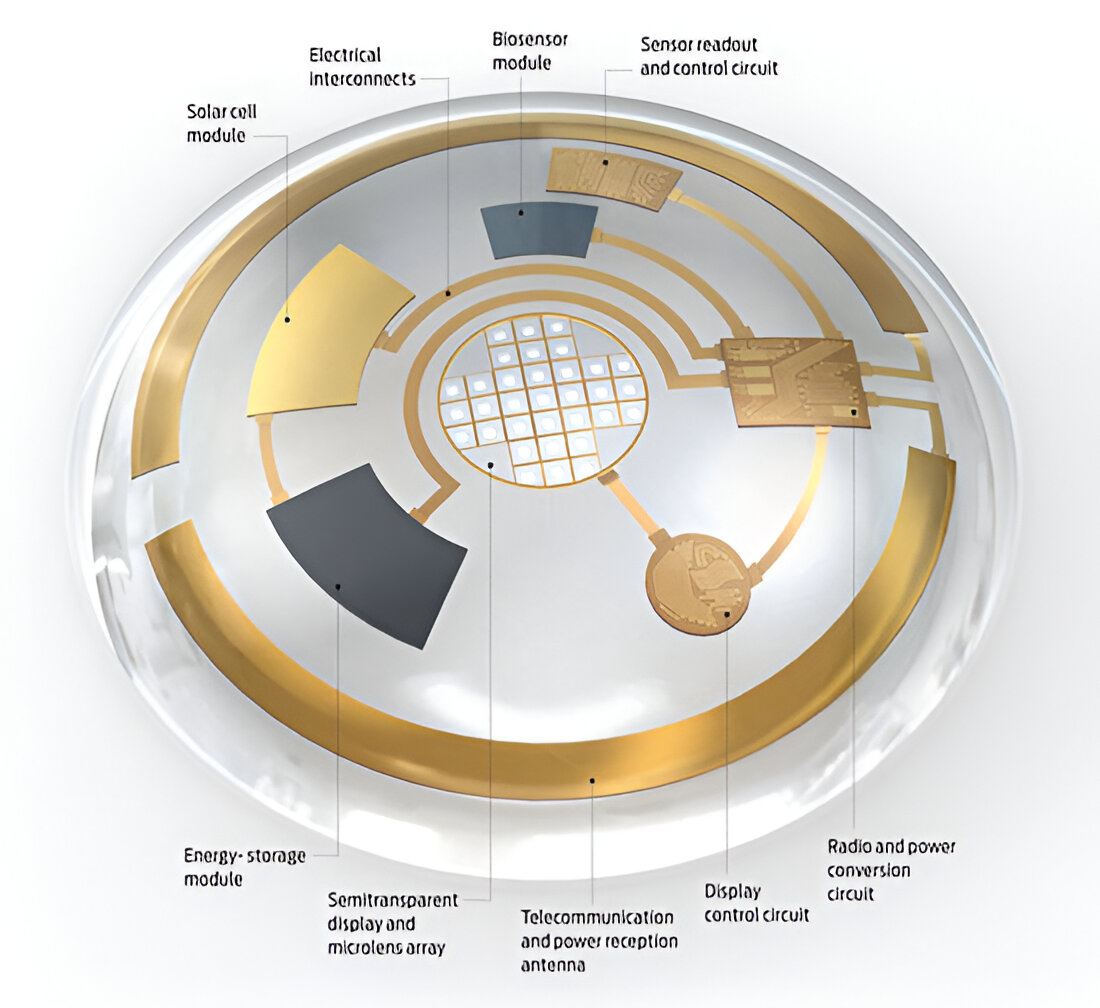
-
Tear glucose levels can provide an alternative to finger-prick testing. Smart lenses could alert users when their sugar levels are too high or low.
Drug Delivery
-
Lenses that release medication in controlled doses could revolutionize treatments for dry eye, corneal ulcers, or allergic conjunctivitis.
Myopia Control
-
Future lenses could combine drug delivery (like atropine) and optical designs to slow down myopia progression in children.
Beyond Health: Augmented Reality and Vision Enhancement
Smart lenses could become the ultimate wearable display. Imagine:
-
Real-time subtitles for translation
-
Navigation overlays during travel
-
Sports data while playing
-
Zoom vision or night vision enhancement for low-light environments
Such capabilities could eventually aid the visually impaired or elderly by enhancing contrast sensitivity, object recognition, and mobility.
Challenges Ahead
While the potential is enormous, several hurdles remain:
-
Miniaturization of components without compromising vision
-
Power supply and battery life
-
Biocompatibility and safety over long-term wear
-
Data privacy and security
-
Regulatory approvals from medical and tech authorities
Smart lenses must pass rigorous clinical trials and FDA or CE certifications before becoming mainstream.
What’s Next?
The next decade will likely witness clinical trials, early-market prototypes, and specialized smart lenses entering niche segments—especially in medical monitoring and sports performance.
As AI integrates with biometric data and 5G/6G networks enable instant connectivity, smart lenses may serve as a personal health assistant, AR tool, and vision enhancer—all in one.
Final Thoughts
Smart contact lenses represent a powerful fusion of vision care and digital innovation. For optometrists, ophthalmologists, tech developers, and patients alike, they promise a future where eye health, real-time information, and augmented reality converge seamlessly.
The eyes, long called the window to the soul, may soon become windows to the digital world—and smart lenses could be the key to unlocking that vision.